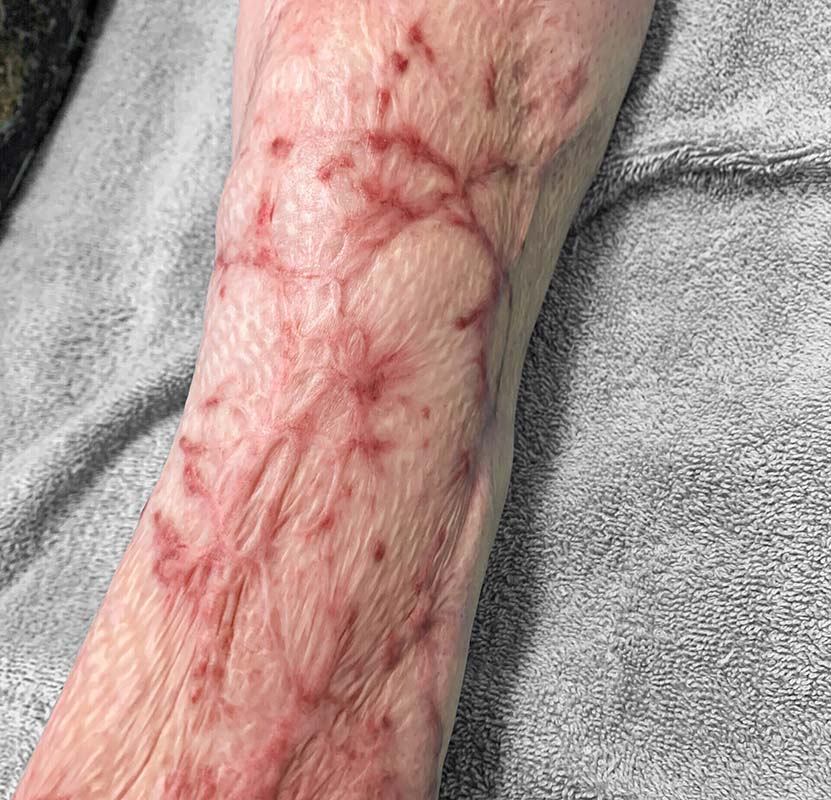
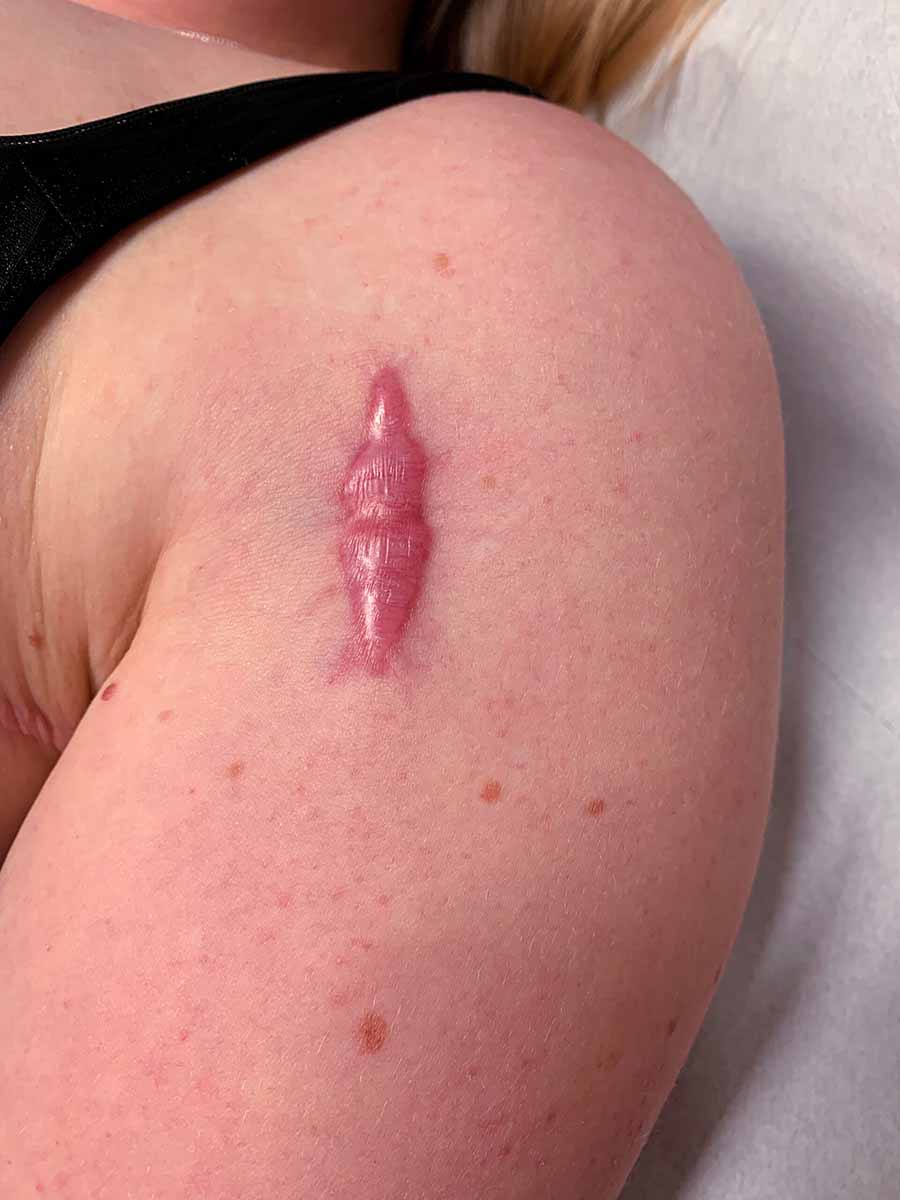
Redness

About Redness
Treatment options for Redness
Skin Camouflage
Skin camouflage creams are a completely non-invasive way of reducing the appearance of scarring whilst undergoing treatment or after treatment is complete. Skin camouflage creams are medical grade, pigmented (contains colour, like a temporary paint for the skin) cream that comes in many colours and can be mixed to match any skin colour. They can be used by any gender or age. Skin camouflage can help increase your confidence by reducing the appearance of your scar and the amount of staring and/or questions from others.
Pressure Therapy
Pressure therapy is a standard treatment to prevent hypertrophic scars (mainly burn scars). Pressure therapy involves wearing garments made from elasticized fabrics or wearing masks/collars made from hard materials maybe with a silicone top layer. The exact reason why pressure works is still not fully understood. It’s thought that pressure controls collagen synthesis and limits the supply of blood, oxygen and nutrients to the scar tissue. It may also have a role in reducing inflammation.
Silicone Therapy
Scars and skin graft donor sites need regular creaming (moisturisation) to prevent the area from drying, cracking and becoming sore. The oil glands in your skin which usually provide moisture can be damaged or destroyed by the injury. The surface layer of the skin which prevents water loss is damaged. Therefore, the healed skin lacks the moisture needed. Silicone works by sealing in the moisture and hydrating the scar. Through providing occlusion (covering) and hydration to the outer layer of the epidermis evaporation of water is reduced from the skin. Silicone treatment aims to flatten, soften and reduce the redness and discomfort of your scar over time. Silicones possess many skin-friendly properties; they are easy to use and remove, painless, can be worn for long periods, are resistant to microbial growth, and are waterproof.
Moisturizers
Moisturisers increase the water content (hydration) of the stratum corneum (top layer of the skin) which fills the spaces between partially desquamated skin flakes and makes the skin appear smoother. In normal skin there is minimal water loss through the epidermis to the surrounding atmosphere. Due to damage to the skin barrier, young and inflamed scars have higher amounts of water loss; this is increased by dry skin. There is a wide range of over-the counter moisturisers available, some products claim to reduce the appearance of scars.
For newly healed wounds and scars that are exposed to sunlight it is vital to use a moisturiser with SPF protection. Because the melanocytes (pigment-cells) are unbalanced and fragile in these areas, they can over-react to normal sun exposure. This can cause the new skin or scar to become permanently darker in colour (hyperpigmented).
Topical Ointments and Creams
Several prescription and over-the-counter topical agents are available, many claim to alleviate symptoms, improve the appearance of scars and accelerate wound healing. Topical therapies have the advantage of being easy to use, are easily available and deliver the ingredients directly to the scar. Patients often decide (maybe based on word of mouth) themselves on which topical agents to use rather than through recommendations from a scar specialist. Topicals are not usually effective on their own and other treatments are also usually necessary. Some information on common topicals is given here:
Scar Massage
Scar massage is a non-surgical technique used in day-to-day scar and burn care. There are multiple techniques that can be used and that are quite easy to apply.
Vacuum Massage
Vacuum massage is also known as depressomassage, vacuotherapy or Endermologie®. It is a non-invasive mechanical massage technique. It is performed with a mechanical device that lifts the skin by suction and creates a skin fold which can be mobilised. In the late 1970s, Louis-Paul Guitay developed the Endermologie® system (or LPG), this uses both suction (negative pressure) and mechanised rollers to mimic manual massage. LPG can provide consistent and effective treatment in a shorter time. Treatment sessions are painless and vary from 10 minutes to longer depending on the state and size of the scar.
Shockwave Therapy
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a type of pulsed acoustic wave resulting from excessive pressure changes. It has been used to treat musculoskeletal diseases (plantar fasciitis, lateral epicondylitis of the elbow, etc.) and wounds. Recent research has shown that ESWT is effective in stimulating biological activities that involve cellular activity. These results suggest that ESWT improves blood perfusion and can be used in tissue regeneration/ scar remodelling. Shockwave treatment is performed without anaesthesia; a treatment head and gel are applied to the area of scar treated.
Scar Taping
Elastic taping (kinesio tape) is an acrylic adhesive that is often used as a physiotherapeutic tool for the treatment of various musculoskeletal problems and other clinical conditions in athletes and patients.
Corticosteroid Therapy
Corticosteroid therapy has been commonly used for years to treat hypertrophic and keloid scars. Corticosteroids suppress inflammation, reduce collagen synthesis and inhibit cell proliferation; itch and thickness of scars is reduced. Corticosteroids can be given through injection, steroid tape or topically (by cream). Intralesional injections (injections into the scar) are common treatments for linear scars, hypertrophic scars and small keloids. Other treatments alongside corticosteroid therapy are often required for large keloids and thick hypertrophic scars.
Micro-Needling
Micro-needling is a semi-invasive technique that can be used on the face and body to achieve collagen induction (production). In this technique the skin or scar is pricked with needles to cause percutaneous collagen induction, this builds up connective tissue underneath retracted (contracted/stuck) or hypertrophic scars and wrinkles.
Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL)
The Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) is a highly effective and low risk laser for the treatment of a wide range of vascular lesions. PDL releases brief pulses of selectively absorbed optical radiation which can cause selective damage to pigmented structures (blood vessels) and cells. The PDL is used to treat port-wine stains, facial telangiectasias and haemangioma. Newer PDLs with longer wavelengths and extended pulse durations have made deeper tissue penetration possible and improved clinical outcomes with reduced risk. PDL treatments are performed with a topical anaesthetic.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) is not the same as a laser. IPL releases pulses of energy through light in a broad wavelength range which produces heat on the skin. A laser projects energy in a very narrow wavelength range which is more focused and therefore produces bleeding (purpura). Thanks to the broad wavelength range, IPL gives less focused heat which reduces the amount of bleeding. The light targets haemoglobin in red blood cells which aims to close the local vessels and reduce the blood supply to the growth of the scar tissue.
Surgical Wound Closure Techniques
The healing of cutaneous wounds after surgery is the result of a cascade of complex biochemical events that can be categorized into four overlapping phases: haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodelling. All these phases of wound healing are influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic (inside and outside) mechanical forces which effect the tension in the skin. Evidence shows that extracellular matrix remodelling can be upset by these forces. For example, wounds over or near joints may be more likely to develop hypertrophic scars because of joint movements causing repeated tension on the wound, leading to abnormal scarring.