Surgical Wound Closure Techniques
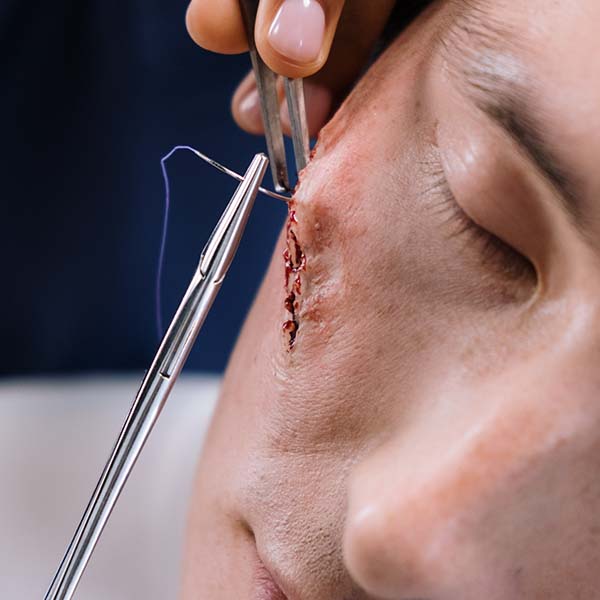
The healing of cutaneous wounds after surgery is the result of a cascade of complex biochemical events that can be categorized into four overlapping phases: haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodelling. All these phases of wound healing are influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic (inside and outside) mechanical forces which effect the tension in the skin. Evidence shows that extracellular matrix remodelling can be upset by these forces. For example, wounds over or near joints may be more likely to develop hypertrophic scars because of joint movements causing repeated tension on the wound, leading to abnormal scarring.
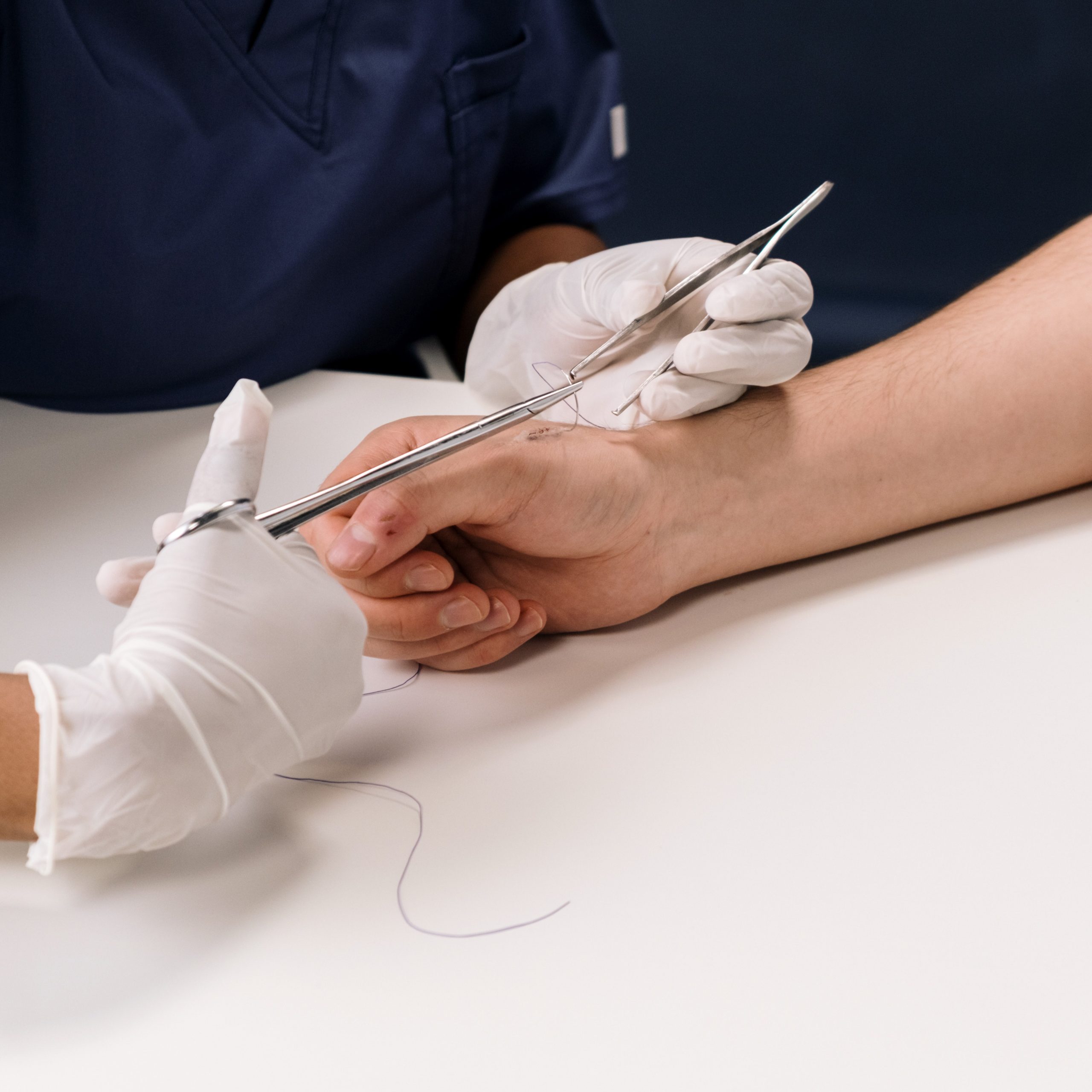
Suture techniques to minimize dermal tension
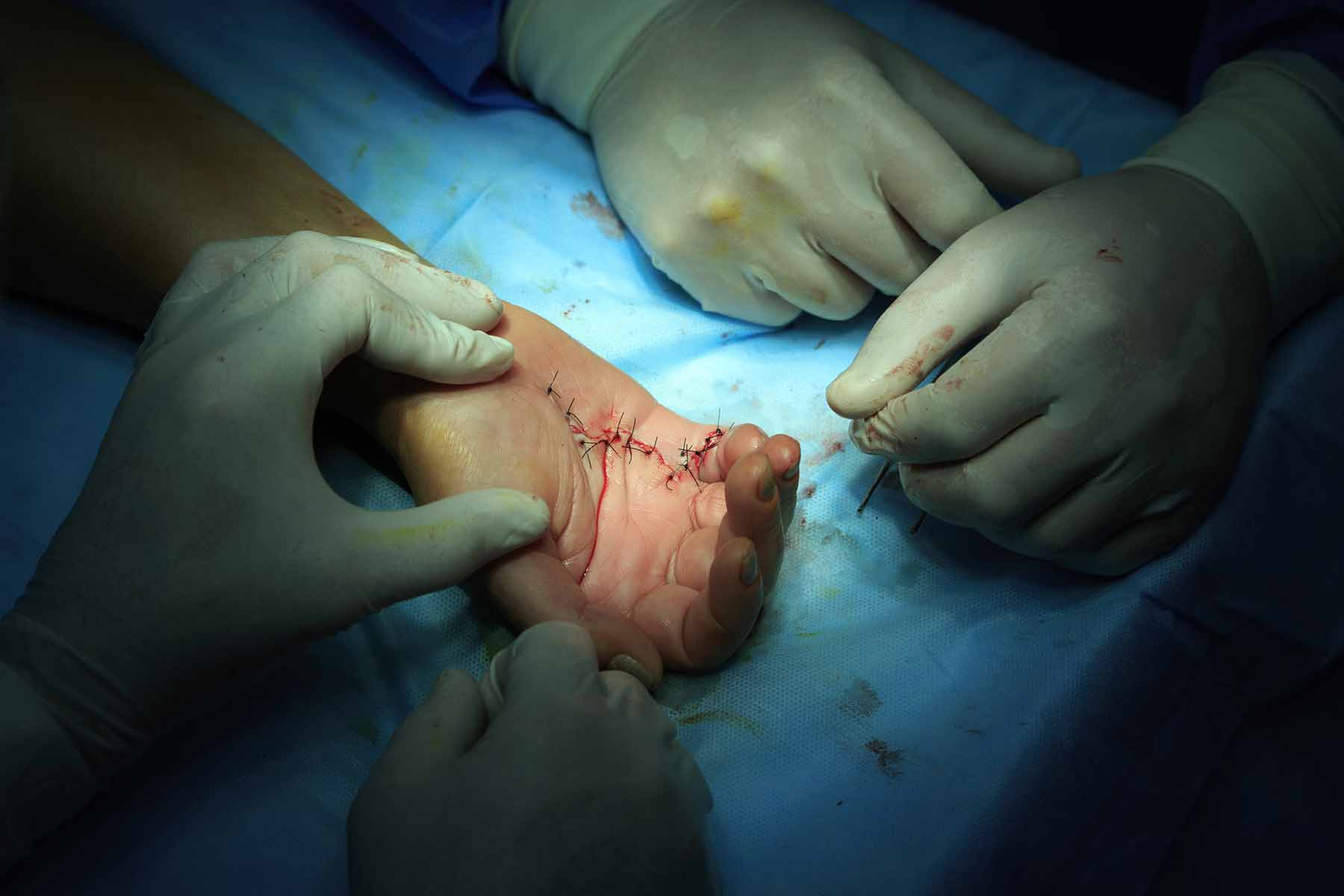
Dermal sutures alone do not effectively reduce tension on the dermis; deeper structures such as the superficial and deep fascia also need suturing. A study showed that deep fascia suturing reduced about 90% of tension on the wound edge, while superficial fascia suturing reduced the remaining 10% of the tension.
Z-Plasty
Another way to prevent pathological scar formation in high-tension areas is to use zigzag suturing techniques such as the Z-plasty. Z-plasty is particularly suitable for joint or limb surgery because the fatty tissue layer in these areas is thin: this means that it is difficult to find the superficial fascia and apply the subcutaneous/ fascial tensile reduction sutures.
F.A.Q.